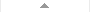1660 Head and Neck
This 3D printed specimen of a parasagittally sectioned head and neck demonstrates a range of anatomical features:
Lateral aspect of the face: A window has been created to expose the parotid region. The pinna of the ear has been left intact, however the mastoid process has been exposed by reflection of the sternocleidomastoid (SCM) muscle. The parotid gland has been carefully removed to display structures which are normally embedded or hidden by the gland. The attachment of the posterior belly of digastric arising from the digastric groove medial to the mastoid process can be clearly seen. The masseter muscle is identifiable as it inserts into the lateral surface of the ramus and angle of the mandible. The condyle of the mandible can be seen in an opened temporomandibular joint (TMJ). The articular disc of the TMJ is indicated by a blue/grey colouration. The external carotid artery (ECA) can be seen passing deep to the digastic muscle and tendon. The branches of the ECA including facial artery, the maxillary artery, occipital artery and posterior auricular artery are preserved. At the inferior aspect of the dissected window one can see the cut remains of the internal jugular vein (IJV) and the cut upper surface of the submandibular gland and the hypoglossal nerve winding around the ECA on its lateral surface. The vagus nerve is just visible between the ECA/common carotid and the IJV. Emerging posterior to digastric one can see the spinal part of the accessory nerve superficial to the levator scapulae muscle (stretched due to the manner in which the SCM has been reflected).
The facial nerve can be seen emerging from the stylomastoid foramen immediately posterior to the styloid process and dividing into temporal, zygomatic, buccal and marginal mandibular branches on the face.
The branches of the trigeminal that supply the dermatomes of the face are illustrated diagramatically by painted nerves on the skin of the face.
Brain and cranial cavity: The medial surface of the cerebrum with the corpus collosum and thalamus are demonstrated. The septum pelucidum has been removed. The left hemisphere of the cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres have been removed to expose the floor of the left anterior, middle and posterior cranial fossa and the fourth ventricle. The anatomy around the cavernous sinus and sella turcica is well displayed. The intracranial course of cranial nerves II, III, V, VII, VIII, IX, X and spinal part of XI are also highlighted from their origin from the brainstem. The facial canal has been opened by removal of part of the temporal bone to expose the facial nerve, the geniculate ganglion and its course in the middle ear (due to removal of the tegmen tympani).
Medial surface: The parasagittal cut surface shows the lateral ventricle, the right cerebral peduncle, posterior cerebral artery, and the cut edge of the tentorium cerebelli. In the region of the sphenoid the internal carotid artery and the carotid siphon are visible in the cavernous sinus as it pierces the dural roof (pale green) to commence its intracranial course. Here it lies lateral to the right optic chiasm. The mouth, tongue, associated muscles, lateral aspect of the nasal cavity, nasopharynx, and cut muscles and vertebrae are also visible on the medial surface of this parasagittal section.
<번역>
이 3D 프린팅된 패러사이트 분할 머리와 목 샘플은 다음과 같은 다양한 해부학적 특징을 보여줍니다.
얼굴 측면: parotid 영역을 노출하기 위한 창이 생성되었습니다. 귀의 핀나는 온전하게 유지되었지만 유방돌기는 흉골근(SCM)의 반사에 의해 노출되었다. 일반적으로 글랜드에 내장되거나 숨겨져 있는 구조를 표시하기 위해 이하선을 조심스럽게 제거했습니다. 이복구 내측에서 유두돌기로의 이복구 후복부의 부착을 명확하게 볼 수 있다. 마사지 근육은 라무스의 측면 표면과 하악골의 각도에 삽입되기 때문에 식별할 수 있다. 하악골의 연골은 열린 턱관절(TMJ)에서 볼 수 있습니다. TMJ의 관절 디스크는 파란색/회색으로 표시됩니다. 외경동맥(ECA)이 이완근과 힘줄로 깊숙이 지나가는 것을 볼 수 있다. 안면동맥, 상악동맥, 후두동맥 및 후이동맥을 포함한 ECA의 가지를 보존한다. 절개된 창문의 아래쪽 측면에서는 내경정맥(IJV)의 절단 잔부와 그 측면의 ECA에 감긴 턱밑샘의 절단 상면을 볼 수 있다. 미주신경은 ECA/공통경동맥과 IJV 사이에서만 볼 수 있다. 이복부 후면에서 부상하는 부신경의 척추부분을 레베이터 견갑골근(SCM이 반사된 방식에 의해 늘어짐) 표면으로 볼 수 있다.
안면신경은 기형돌기 바로 뒤에 있는 문형골공에서 나와 얼굴의 측두엽, 광대뼈, 구강 및 주변 하악골 가지로 나뉘는 것을 볼 수 있다.
얼굴의 피부를 공급하는 삼차수의 가지는 얼굴 피부에 그려진 신경으로 도식적으로 묘사된다.
뇌와 두개강: 콜로슘과 시상체가 있는 대뇌의 내측 표면이 입증되었다. 중격 펠루시텀이 제거되었습니다 소뇌와 대뇌 반구의 좌뇌를 제거하여 좌전방, 중후방 두개와와 제4뇌실의 바닥을 드러냈습니다. 동굴 부비강과 터시카 팔 주변의 해부도가 잘 보입니다. XI의 두개 신경 II, III, V, VII, VII, VII, IX, X 및 척추 부분의 두개 내 과정도 뇌간으로부터의 기원에서 강조된다. 안면관은 안면신경, 관절신경절 및 중이에 있는 그 경로를 노출시키기 위해 측두골의 일부를 제거함으로써 개방되었다.
중앙 표면: 파라사시탈 절단면에는 측심실, 우뇌페둔클, 후뇌동맥, 소뇌 천막의 절단 가장자리가 표시됩니다. 구상체 영역에서는 경동맥과 경동맥 사이폰이 경막 지붕(경막 녹색)을 관통하여 두개 내 과정을 시작할 때 동굴동 내에 보인다. 이것은 오른쪽 시신경 옆에 있습니다. 입, 혀, 관련 근육, 비강의 외측면, 비인두, 절단된 근육과 척추도 이 파라시탈 부분의 안쪽 표면에 보입니다.











 보건교육지원센터를 시작페이지로!
보건교육지원센터를 시작페이지로!  즐겨찾기
즐겨찾기